XJTLU team breaks its own world record in post-quantum security analysis
A team at Xi’an Jiaotong-Liverpool University has again raised the bar in cybersecurity research by breaking its own world record in solving the lattice Shortest Vector Problem (SVP), a fundamental mathematical problem in quantum-resistant cryptography.

Researchers from XJTLU’s Post-Quantum Migration Interdisciplinary Lab (PQC-X) have solved the Darmstadt 210-dimensional SVP challenge, which has very important implications for the long-term security of the digital economy including banking and critical infrastructures in the new quantum era.
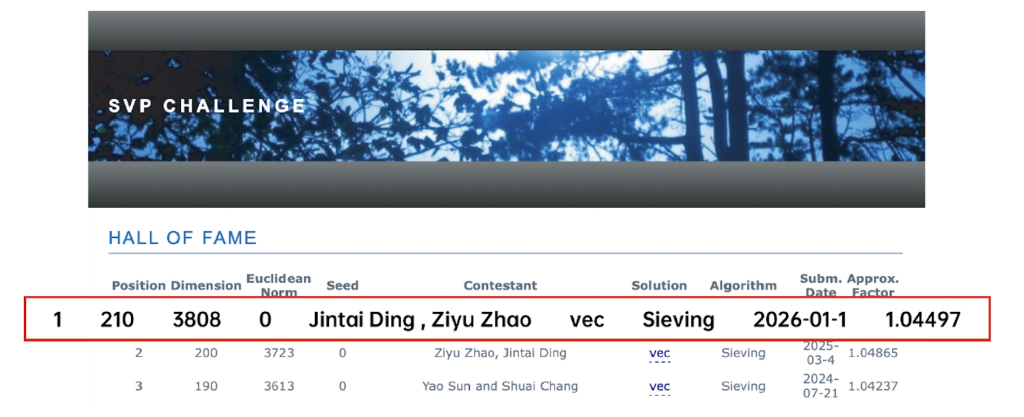
The achievement – recently announced at a post-quantum cryptography conference in Nanjing, capital of Jiangsu province – follows the XJTLU team’s solving the 200-dimensional SVP challenge in March 2025 and the post-quantum Kyber-208 challenge in November 2025.
Rapid advancements in quantum computing pose a serious threat to existing public key cryptography, the security foundation of global modern communication systems including the internet and the financial systems, making the search for alternative quantum resistant solutions a global priority. Lattice-based cryptography is currently seen as the most promising next-generation cryptographic standard capable of safeguarding sensitive data from quantum computer attacks, which is fully demonstrated in the security standards developed recently by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the US.
Professor Jintai Ding, director of PQC-X and Dean of XJTLU’s School of Mathematics and Physics, says his team uses an “attack-to-defend” model, aiming to conduct high-intensity pressure testing on existing mathematical defence to build a solid security foundation for the next generation post-quantum security standards.

Professor Jintai Ding
He explains that solving the 210-dimensional SVP provides key parameter correction evidence and support for global post-quantum cryptography standards to truly verify the reliability and the security of these future protocols.
This work is partially supported by the “Research on Quantum-Resistant Cryptography Migration Technology for Banking and Critical Infrastructure” grant from the National Key R&D Program of China, where Professor Ding is the Lead of sub-project 1. At the Nanjing conference, Chengjun Zhou, President of the Jiangsu Society for Finance and Banking and the project lead, stated that the project brings together strengths from industry, academia, research, and application sectors to achieve advances in quantum-resistant cryptography algorithms, hardware and software implementations, security protocols, and quantum security risk management.

Chengjun Zhou
He noted that the quantum-resistant transformation of financial systems is a very complex process involving comprehensive upgrades of existing public key cryptosystems, communication protocols, and risk management systems.
Dr Yimin Ding, Vice President of XJTLU, stated in his speech that XJTLU firmly believes higher education institutions should not only pursue academic frontiers within the national innovation system but also respond to the urgent needs of the nation and the industry. Leveraging its PQC-X lab, XJTLU promotes the deep integration of multi-disciplinary collaborative research with real-world financial scenarios, committing to transforming scientific achievements into implementable and scalable security solutions.

Dr Yimin Ding
The conference also saw representatives from the China Construction Bank, CITIC Bank, and the Bank of Jiangsu demonstrate application validation results. A panel of experts from leading research institutes and industry organisations concluded that the XJTLU team’s achievement in the project was indeed state-of-the-art in the field of lattice-based cryptography security analysis.
By Qinru Liu
Edited by Patricia Pieterse
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.
